Grubbs' Outlier Test
Grubbs' outlier test (Grubbs 1969  and Stefansky 1972 and Stefansky 1972  ) checks normally distributed data for outliers. This implies that one has to check whether the data show a normal distribution before applying the Grubbs test. The Grubbs test always checks the value which shows the largest absolute deviation from the mean. If an outlier has been identified and removed, the test must not be repeated without adapting the critical value. ) checks normally distributed data for outliers. This implies that one has to check whether the data show a normal distribution before applying the Grubbs test. The Grubbs test always checks the value which shows the largest absolute deviation from the mean. If an outlier has been identified and removed, the test must not be repeated without adapting the critical value.
The application of the test is quite simple and straightforward: one searches the maximum of the absolute differences between the values xi and the mean  . The result is divided by the standard deviation of the sample. If the resulting test statistic g is greater than the critical value, the corresponding value can be regarded to be an outlier. An extract of the critical values is shown in the following table: . The result is divided by the standard deviation of the sample. If the resulting test statistic g is greater than the critical value, the corresponding value can be regarded to be an outlier. An extract of the critical values is shown in the following table:

| n |
gcrit
α=0.05 |
gcrit
α=0.01 |
|
n |
gcrit
α=0.05 |
gcrit
α=0.01 |
|
n |
gcrit
α=0.05 |
gcrit
α=0.01 |
| 3 | 1.1543 | 1.1547 | | 15 | 2.5483 | 2.8061 | | 80 | 3.3061 | 3.6729 |
| 4 | 1.4812 | 1.4962 | | 16 | 2.5857 | 2.8521 | | 90 | 3.3477 | 3.7163 |
| 5 | 1.7150 | 1.7637 | | 17 | 2.6200 | 2.8940 | | 100 | 3.3841 | 3.7540 |
| 6 | 1.8871 | 1.9728 | | 18 | 2.6516 | 2.9325 | | 120 | 3.4451 | 3.8167 |
| 7 | 2.0200 | 2.1391 | | 19 | 2.6809 | 2.9680 | | 140 | 3.4951 | 3.8673 |
| 8 | 2.1266 | 2.2744 | | 20 | 2.7082 | 3.0008 | | 160 | 3.5373 | 3.9097 |
| 9 | 2.2150 | 2.3868 | | 25 | 2.8217 | 3.1353 | | 180 | 3.5736 | 3.9460 |
| 10 | 2.2900 | 2.4821 | | 30 | 2.9085 | 3.2361 | | 200 | 3.6055 | 3.9777 |
| 11 | 2.3547 | 2.5641 | | 40 | 3.0361 | 3.3807 | | 300 | 3.7236 | 4.0935 |
| 12 | 2.4116 | 2.6357 | | 50 | 3.1282 | 3.4825 | | 400 | 3.8032 | 4.1707 |
| 13 | 2.4620 | 2.6990 | | 60 | 3.1997 | 3.5599 | | 500 | 3.8631 | 4.2283 |
| 14 | 2.5073 | 2.7554 | | 70 | 3.2576 | 3.6217 | | 600 | 3.9109 | 4.2740 |
There is a one-sided alternative which allows to test either the minimum xmin or the maximum xmax of the entire data set. The test statistics calculates according to the following formulas:

A value can be regarded an outlier if the statistic g is greater than the critical value. Please note that in the case of the one-sided test the critical values are different. An extract is given below:
| n |
gcrit
α=0.05 |
gcrit
α=0.01 |
|
n |
gcrit
α=0.05 |
gcrit
α=0.01 |
|
n |
gcrit
α=0.05 |
gcrit
α=0.01 |
| 3 | 1.1531 | 1.1546 | | 15 | 2.4090 | 2.7049 | | 80 | 3.1319 | 3.5208 |
| 4 | 1.4625 | 1.4925 | | 16 | 2.4433 | 2.7470 | | 90 | 3.1733 | 3.5632 |
| 5 | 1.6714 | 1.7489 | | 17 | 2.4748 | 2.7854 | | 100 | 3.2095 | 3.6002 |
| 6 | 1.8221 | 1.9442 | | 18 | 2.5040 | 2.8208 | | 120 | 3.2706 | 3.6619 |
| 7 | 1.9381 | 2.0973 | | 19 | 2.5312 | 2.8535 | | 140 | 3.3208 | 3.7121 |
| 8 | 2.0317 | 2.2208 | | 20 | 2.5566 | 2.8838 | | 160 | 3.3633 | 3.7542 |
| 9 | 2.1096 | 2.3231 | | 25 | 2.6629 | 3.0086 | | 180 | 3.4001 | 3.7904 |
| 10 | 2.1761 | 2.4097 | | 30 | 2.7451 | 3.1029 | | 200 | 3.4324 | 3.8220 |
| 11 | 2.2339 | 2.4843 | | 40 | 2.8675 | 3.2395 | | 300 | 3.5525 | 3.9385 |
| 12 | 2.2850 | 2.5494 | | 50 | 2.9570 | 3.3366 | | 400 | 3.6339 | 4.0166 |
| 13 | 2.3305 | 2.6070 | | 60 | 3.0269 | 3.4111 | | 500 | 3.6952 | 4.0749 |
| 14 | 2.3717 | 2.6585 | | 70 | 3.0839 | 3.4710 | | 600 | 3.7442 | 4.1214 |
|

 Statistical Tests
Statistical Tests  Outlier Tests
Outlier Tests  Grubbs' Outlier Test
Grubbs' Outlier Test Statistical Tests
Statistical Tests  Outlier Tests
Outlier Tests  Grubbs' Outlier Test
Grubbs' Outlier Test

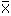 . The result is divided by the
. The result is divided by the 
